The Times of India Article Rating
The Times of India Article RatingNationalism and media- A historical overview and analysis
- Bias Rating
50% Medium Conservative
- Reliability
35% ReliableAverage
- Policy Leaning
50% Medium Conservative
- Politician Portrayal
6% Negative
Continue For Free
Create your free account to see the in-depth bias analytics and more.
Continue
Continue
By creating an account, you agree to our Terms and Privacy Policy, and subscribe to email updates. Already a member: Log inBias Score Analysis
The A.I. bias rating includes policy and politician portrayal leanings based on the author’s tone found in the article using machine learning. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral.
Sentiments
16% Positive
- Liberal
- Conservative
| Sentence | Sentiment | Bias |
|---|---|---|
Unlock this feature by upgrading to the Pro plan. | ||
Reliability Score Analysis
Policy Leaning Analysis
Politician Portrayal Analysis
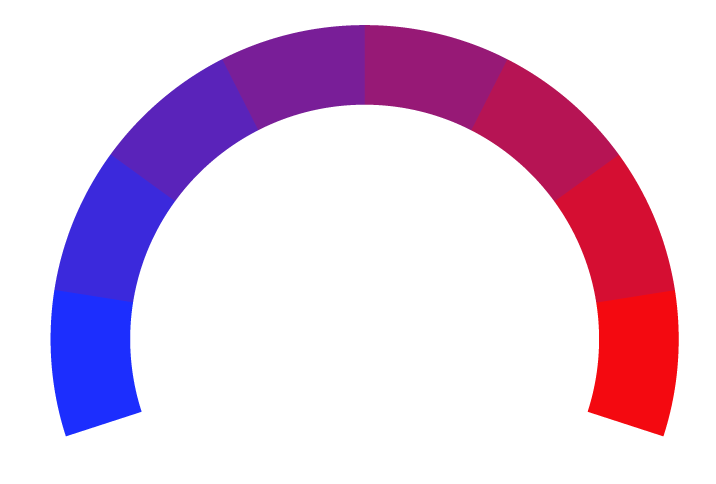
Bias Meter
Extremely
Liberal
Very
Liberal
Moderately
Liberal
Somewhat Liberal
Center
Somewhat Conservative
Moderately
Conservative
Very
Conservative
Extremely
Conservative
-100%
Liberal
100%
Conservative
Contributing sentiments towards policy:
64% : Historical debates- early theories of nationalism and media The classic literature on nationalism, such as works by Hans Kohn, Karl Deutsch, and Benedict Anderson, laid the foundation for understanding how nations are formed.62% : However, digital media has also facilitated the rise of new forms of nationalism, particularly in the context of populist movements.
61% : The continued relevance of nationalism in media While the globalizing force of digital media is undeniable, research shows that national frameworks continue to inform media production, regulation, and consumption.
57% : These scholars placed nationalism within a broader socio-economic and political context but varied in their emphasis on media's role.
57% : This focus on media's role in both unifying and dividing populations within a nation led to more nuanced understandings of nationalism and media.
57% : Nationalism in the digital age - new frontiers The rise of digital technologies has profoundly impacted the relationship between media and nationalism.
57% : While right-wing populist movements often harness nationalist rhetoric, nationalism itself remains a broad and established belief system that affects people's identities and behaviors on a daily basis.
56% : In the digital age, nationalism persists not only in overt political movements but also in everyday interactions and the infrastructure of the online world.
54% : Gellner argued that the very pervasiveness of modern communication technologies, such as print and broadcast media, created the conditions necessary for the rise of nationalism, regardless of the specific content.
49% : In an increasingly interconnected world, the future of media and nationalism will likely continue to evolve, but national frameworks are likely to remain a critical lens through which people make sense of the world.
47% : Despite this, Michael Skey cautions against conflating nationalism with extremism.
46% : Media, nationalism, and the fFuture The relationship between media and nationalism remains complex and multifaceted.
45% : MORE The relationship between nationalism and media has been a topic of both significant historical debate and contemporary relevance.
*Our bias meter rating uses data science including sentiment analysis, machine learning and our proprietary algorithm for determining biases in news articles. Bias scores are on a scale of -100% to 100% with higher negative scores being more liberal and higher positive scores being more conservative, and 0% being neutral. The rating is an independent analysis and is not affiliated nor sponsored by the news source or any other organization.