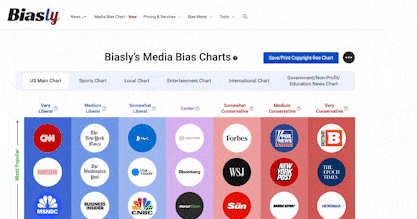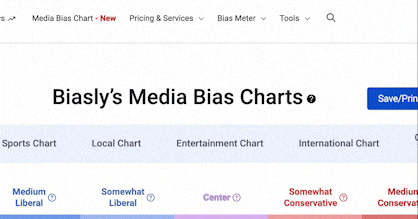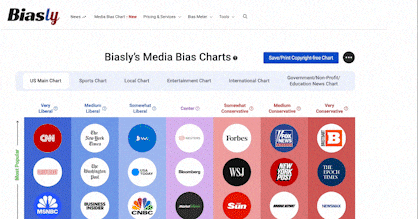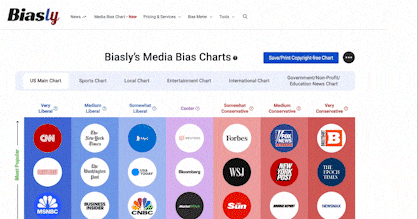
Upon recently being dropped by its primary network Verizon, the reliability of One American News (OAN/OANN) has lately been questioned. Research from the New York Times estimates that OAN can potentially lose 20 million viewers– this begs the question: is the reliability of OAN a cause for concern?
At Biasly, we seek to determine the reliability and accuracy of media companies, providing an upfront analysis and rating system using Biasly’s reliability check. While we previously rated OAN with an A.I bias score of “Moderately Conservative,” what does this mean for their reliability?
Does Reliability Matter?
Reliability refers to how trustworthy or accurate information, or in this case, a news source is. If we consider this definition, it quickly becomes clear why reliability is important in media sources. If we can’t trust the things we read then there isn’t much of a point in continuing to consume content from that source, after all. So how exactly can we gauge the reliability of a news source anyways?
There are several potential measures of reliability to look out for when trying to determine whether a media source is reliable or not. Red flags for an unreliable article can include the presence of wild unsubstantiated claims, facts dependent on other unreliable sources, heavy use of opinionated language, and more. Some indicators of a reliable news source, on the other hand, include things like:
- Absence of subjective/opinionated language in articles
- Credible sources cited (e.g., neutral sources, .gov, .edu websites)
- Facts and statistics backed by multiple relevant outside sources
- Use of primary sources when possible (e.g., interviews, quotes)
- Information that remains consistent across news sources
Just How Reliable is OAN Media?
The political reliability index developed by Biasly objectively assesses news organizations’ accuracy and trustworthiness. One American News Network’s (OAN/OANN) overall Reliability Score has been rated as ‘Fair’ by Biasly. This rating is a weighted average of two distinct scores: the Fact Analysis Score and the Source Analysis Score, each evaluating separate components of OAN’s Reliability. When computing the Average Reliability of the article the Fact Analysis score is more heavily weighted. These ratings are as follows in the next two paragraphs:
OAN’s Fact Analysis Score is ‘Good,’ which suggests readers can trust most of OAN’s content online. The Fact Analysis score focuses more on the accuracy of claims, facts, and sources presented in the article and any hints of selection and omission bias, which we will discuss further in the article.
OAN’s Source Analysis Score is ‘Fair,’ which suggests readers can trust some of the sources, links, and quotes provided by the news source. This score, which is based on A.I., focuses on assessing the quality of sources and quotes used including their number, lengths, uniqueness, and diversity.
However, since these scores are based on percentages and averages, individual articles could be more or less trustworthy depending on the context, author, and other factors. Our findings show that OAN’s reliability is mostly but not all factual because they have retracted several stories in the past or had pieces that were not factual.
Let us analyze the supporting data for OAN’s rankings and discuss what to watch out for while searching for trustworthy news sources.
OAN Media Accuracy and Reliability
Taking a deep dive into the accuracy and factuality of OAN’s articles and scanning for selection and omission bias will allow readers to have full transparency of OAN’s reliability as a news source.
Selection bias is when stories and facts are selected or deselected, often on ideological grounds, to create a narrative in support of the new source’s ideology.
Omission bias, on the other hand, is when different opinions and political views regarding a situation are left out so that the reader is only exposed to the ideological perspective supported by the author. It’s important to keep in mind these two types of biases when trying to assess an article’s level of accuracy.
Biasly rates accuracy and credibility ranging from 1-100%, with 1 being the least accurate and 100 the most accurate. These ratings are determined by measuring claims against fact-checked statements, credible sources used, and other external sources used within an article.
As previously mentioned, OAN’s reliability score of “Good” represents the source’s average, with fluctuations between author bias and article topics– as opinion pieces are significantly more likely to have more opinionated and less fact-based sources.
For example, an article titled “Republican States Lead The Charge in Border Security,” is rated as “Very Conservative.” Regarding selection and omission bias, the author Roy Francis only uses sources favoring a conservative political ideology, such as Governor Bill Lee (R-Tenn) and Governor Jim Phillen (R-Neb), Governor Ron DeSantis (R-Fla.), Governor Tate Reeves (R-Miss) and Governor Greg Abbott (R-Texas).
While the crisis concerns primarily the southern border, Republican-led states are the focus of the article yet, no liberal members of government are consulted or interviewed. Thus, selection and omission bias is present in the article as Francis creates a narrative in support of a conservative ideology by failing to include any input from a liberal member of the government. Also, the article takes strong opinions against illegal immigration, but does not mention any other different opinions regarding the situation, leading to only reporting on the author’s ideological perspective.
Contrastingly, a distinctly fact-based article titled “Department of Homeland Security Announces New Body-Worn Camera Policy For All Its Agencies” quotes the DHS and Homeland Security Secretary and is a very agreeable and reliable article containing no opinionated or questionable statements from the author.
In turn, while some articles may have contentious statements and lower credibility due to unconfirmed facts, other articles can be fully factual and reliable. While Biasly still has a lot of OANN articles to analyze for their credibility and reliability scores, as of right now the company has a modest reliability score of “Good,” which is important to keep in mind when consuming news sources.
Analysis of OAN Online Articles
Taking a further look into the quality of sources and facts used as well as any selection or omission bias present in the articles further demonstrates the reliability of OAN as a source for news. Recall that selection bias involves facts being selected or deselected based on the source’s ideology. Similarly, omission bias leaves out specific opinions and political views to only expose the reader to the ideas the author wants to portray.
Quality of Sources and Facts Used
First, an article titled “US Government Hit During Global Cyberattack” cites several diverse sources, including seven direct quotes, with four short-length quotes and three medium-length quotes. A list of these sources is as follows:
- Executive Assistant Director of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA)
- CISA Cyber Twitter account
- Progress Software, a U.S. firm
- CISA Director Jen Easterly
- US Department of Energy
- CNN
- Johns Hopkins University
- Brett Callow, cybersecurity analyst
While the quality of sources covers a range of popular news reporting sources, to independent analysts and high-level members of CISA, the article remains near-center in terms of the political spectrum. As such, the author can write an informative and reliable article on the cyberattack. If there was more knowledge available about the situation, the author could have gone more in-depth using statistics and pulling from different members of government to have a holistic understanding of the implications for the US government and the safety of their citizens.
Contrastingly, an article titled “The End of Democracy” contains misinformation and makes grasping claims despite no external sources. In calling Biden autocratic, racist and many other offensive terms with zero sources used.
For example, “The president and his agencies repeatedly issue unconstitutional and unlawful mandates, and refuse to enforce laws they don’t like” is a sentence in the article with no additional support or factual evidence. By making these claims with inadequate backup, this is an example of an article that is not reliable.
Selection and Omission Bias
Continuing the article “The End of Democracy”, the article’s sole focus is to tear down the Biden administration and use extreme language toward Democrats. While the article’s ideologies are framed to the right, this reflects a strong selection bias as the author only speaks about the flaws of the Democrats, and selects only information that continues to frame the author’s point of view.
Moreover, with a political portrayal of 100% negative, it is evident that omission bias is used to leave out any positive sentiments towards the Biden administration. With zero positive things to say about Democrats, it is clear that the author wants the reader only to have a Republican-exposed view, clearly indicated by this quote:
“When the president disregards the Constitution and federal law there are only two remedies, The first, is protracted litigation, which Biden side steps by issuing new orders. The other, impeachment, and conviction, is impracticable given the small Republican majority in the House, Democrat control of the Senate, and the chilling fact that Kamala Harris is next in line.”
Additionally, by omitting any comments from a Democratic party point of view, the author refuses to account for the perspective of essentially anyone that does not consider themself a Republican.
By examining facts and the quality of sources used and scanning for selection and omission bias, it becomes clear that not every article you read is reliable.
So, is OAN Reliable?
Just as articles differ between their content and authors, OAN finds itself with a reliability score of “Good,” which is identical to that of NY Times which finds itself on the opposite side of the political spectrum.
While this score varies from article to article and author to author, Biasly can analyze these bias and reliability scores using Biasly’s News Check Chrome extension.
Beyond this, it is critical to have an improved understanding of bias and reliability in articles, especially as it varies between sources. By ameliorating our media literacy, we can also improve our knowledge of media bias which helps us as readers to develop a complete understanding of the text provided.